-
-
- Spiral welded pipe equipment
- High frequency straight seam welded pipe production line
- Hot-rolled seamless pipe equipment
- Ductile iron pipe production line
- Hot push pipe bending equipment
- Hydraulic testing machine
- Beveling machine
- Expander
- Steel pipe straightening machine
- Packaging production line
- Finishing line
-
Accessories for welding machine and medium and high frequency equipment
- Submerged arc welding - wire feeder
- Submerged arc welding - control circuit board
- Cutting machine - cutting head
- High-frequency welding - welding the large arm and small arm
- High-frequency welding - circuit boards and components
- Medium frequency annealing - induction heater
- Anti-corrosion special - medium frequency inductor
-
Hot rolling equipment accessories
- Continuous casting steelmaking spare parts
- Heat-resistant roller
- Heating unit and components
- Spindle connection unit and coupling
- Elastic damping device
- Rolling mill
- 1#, 2#, 3# flying shears
- Entrance guard device
- Other parts of the rolling mill
- Transmission components
- Copperware
- Accessories for water sports equipment
- Cooling accessories
Products -
SolutionThe equipment manufactured by the company is widely used in the processing of basic building materials, aerospace, automobile manufacturing, construction machinery manufacturing, transportation, municipal bridges and hvac, national-level oil pipeline construction, port infrastructure, marine bridge engineering, river dam and embankment construction, green energy and other industrial applications.

-
About usSichen Machinery is a global provider of automation solutions for metallurgical equipment, mainly engaged in the research, development, production, and sales of metallurgical products such as rolling mills and pipe-making equipment.

-
ServiceThe company will rely on a large number of technical research and development and on-site commissioning experience accumulated in the manufacture of various equipment in the past two decades, relying on the domestic and international markets, and is committed to providing high-quality products and services to the majority of users.









Share
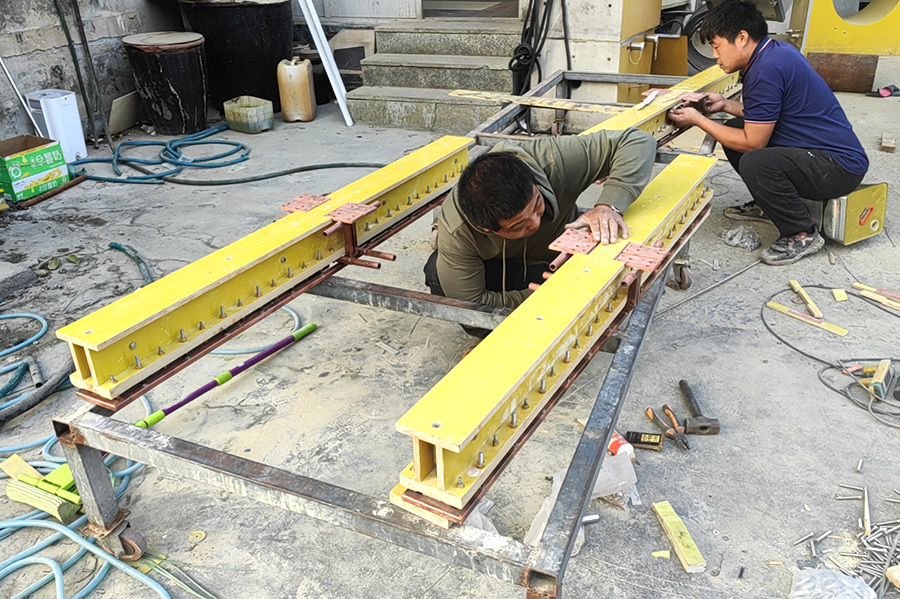
High-frequency welded H-beam production line - medium-sized
Still deciding? If you are interested, you need to take a sample first, Contact us!
Product Category
High-frequency welded H-beam production line
Tags
Metallurgical heavy machinery and equipment
- Product description
- Homepage Product - Related Calls
-
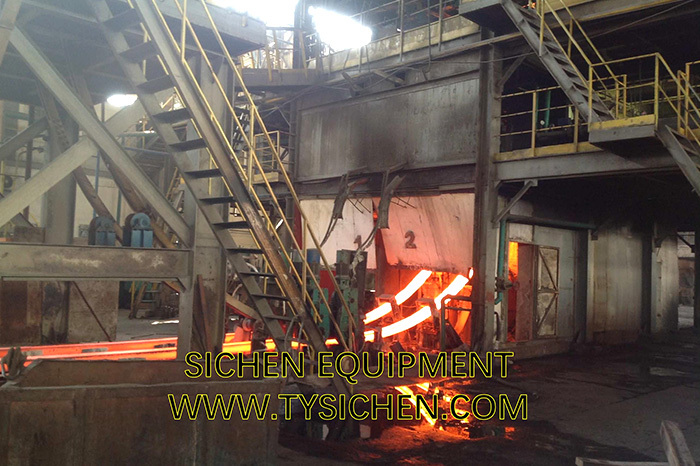
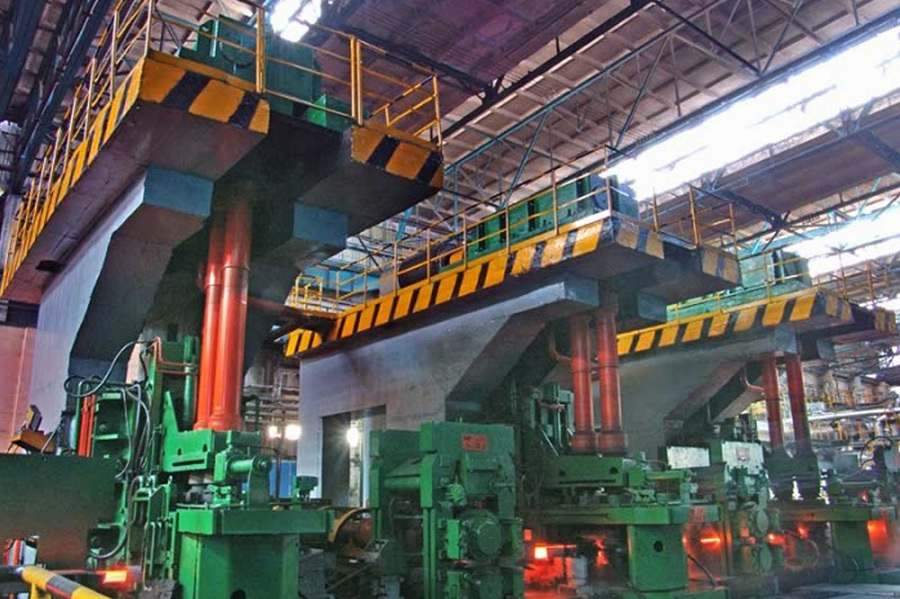
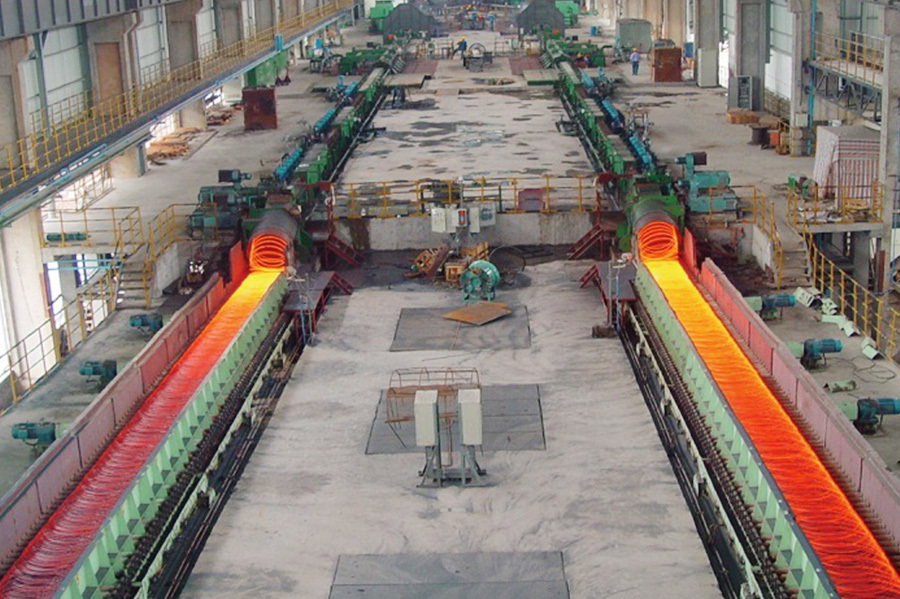
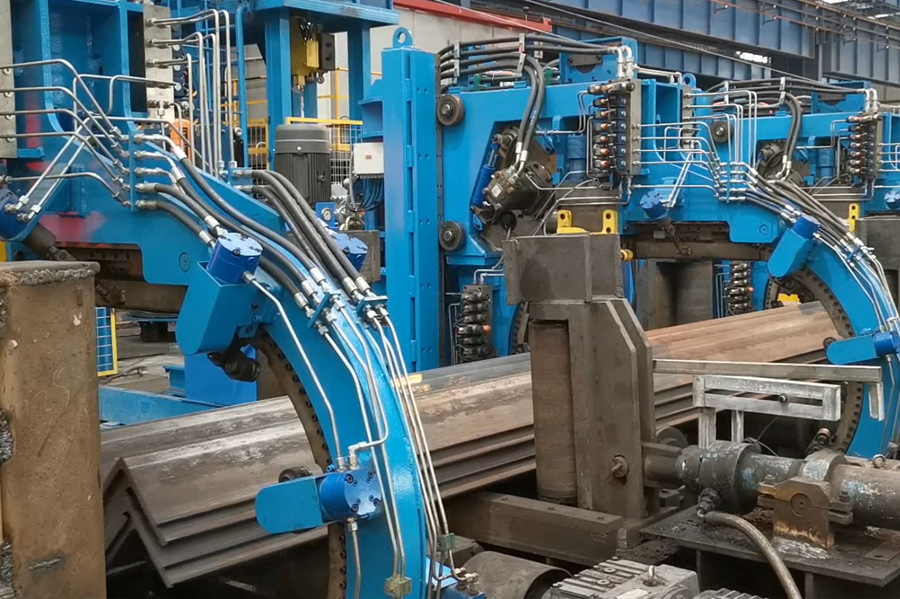
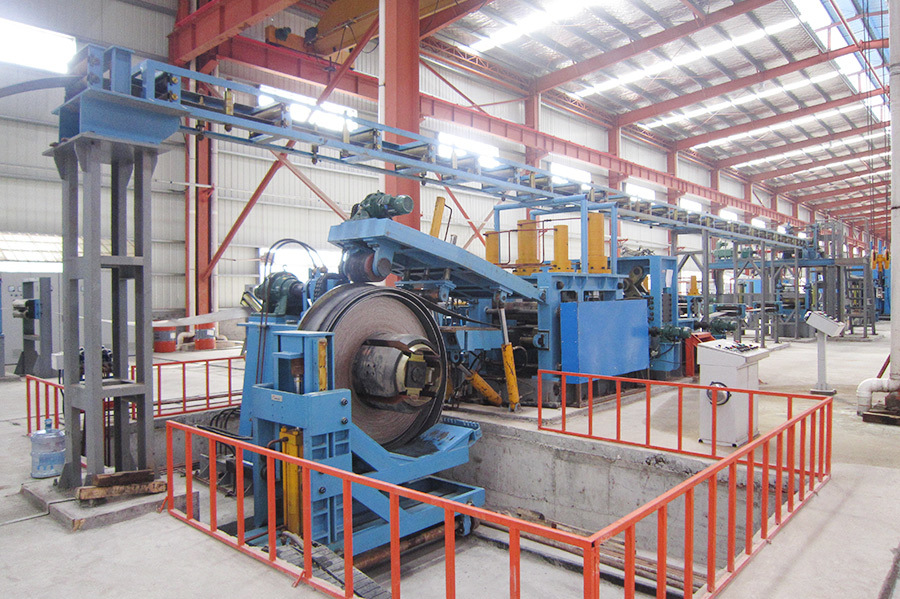
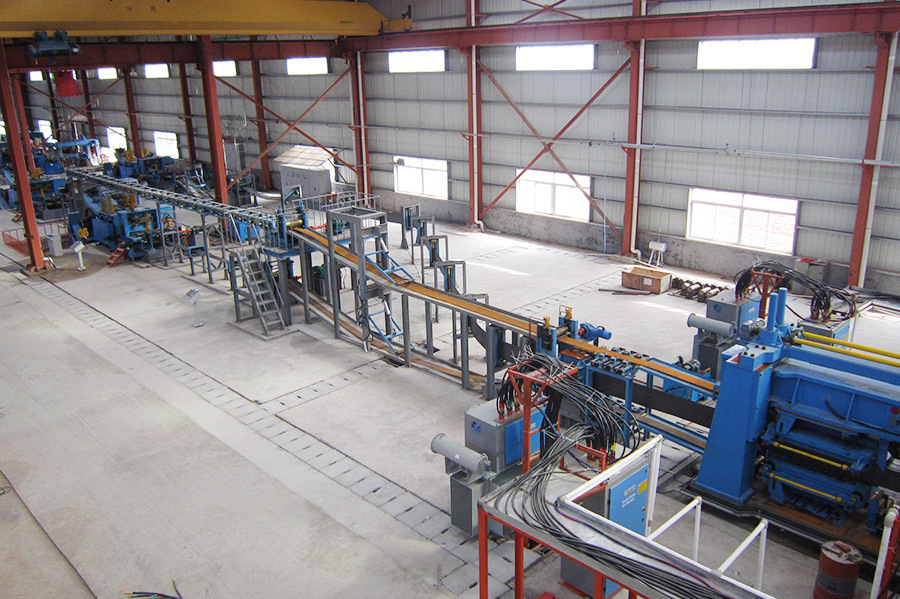
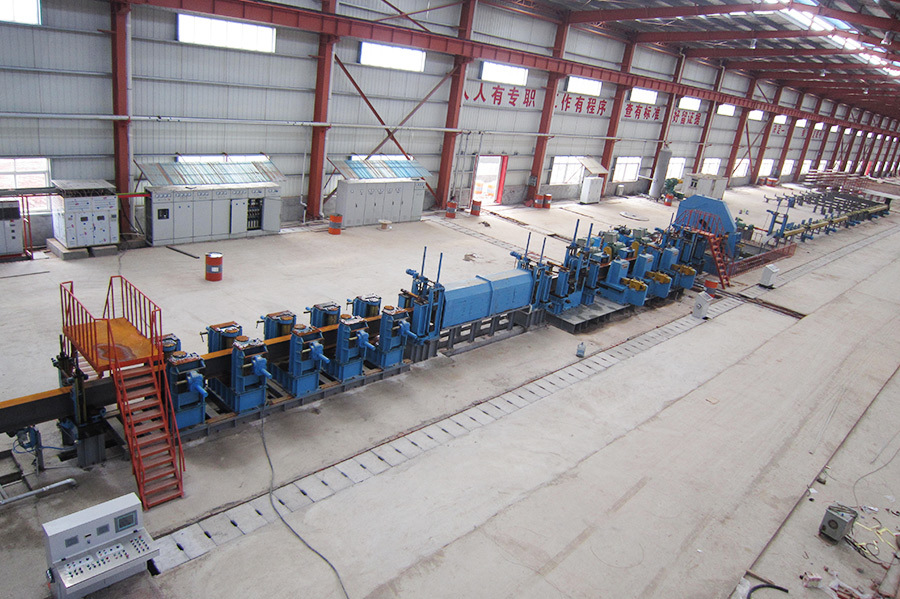
Equipment Introduction
The main technical principle in the high-frequency welding of H-beams is to use high-frequency current to directly heat the upper and lower flange plates and web plates at the welding joint, causing the base material to fuse. Then, it is formed by pressure welding rollers. Heating is concentrated at the welding point, the heat-affected zone is small, and no welding rods or fluxes are used in the welding process. Therefore, the H-beam produced has flat flanges, high precision, and a beautiful appearance.
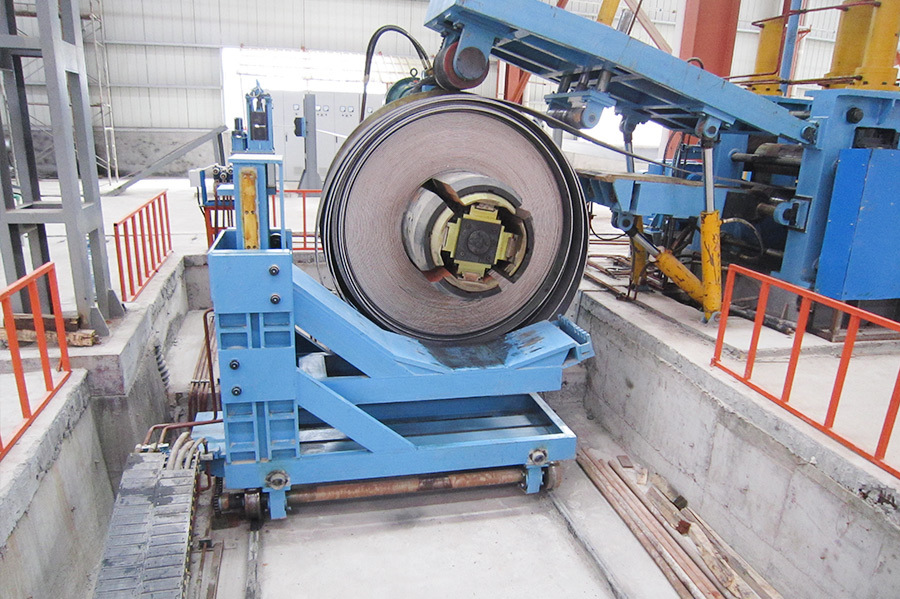
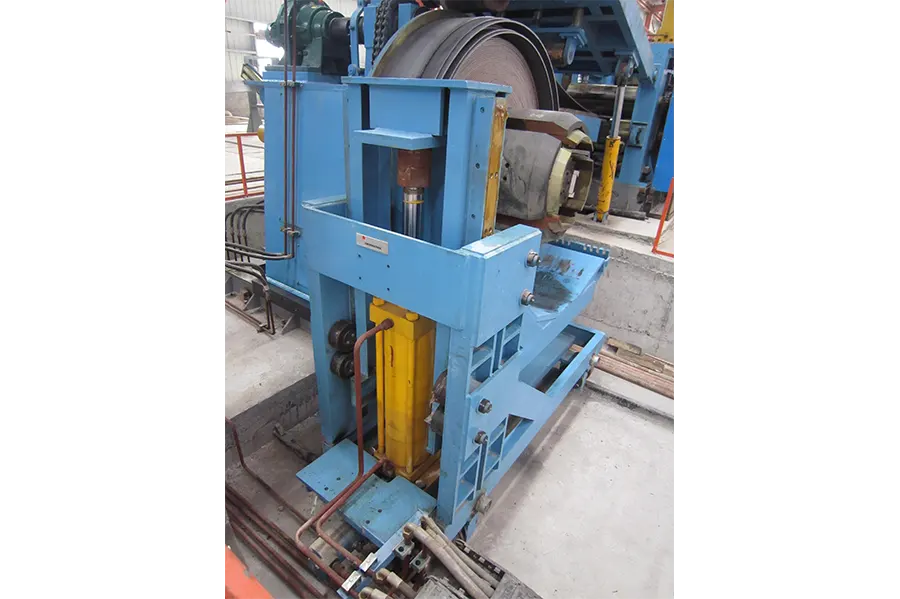
The slit coil is transported from the coil storage area to the coil carriage. This coil is sent to the center position of the decoiler by an electric-powered coil carriage. The coil is loaded onto the decoiler by expanding it with a hydraulic power shaft. The coil head flattening machine flattens the coil head, making it easy to be gripped by the gripping roller and fed into the straightening machine.
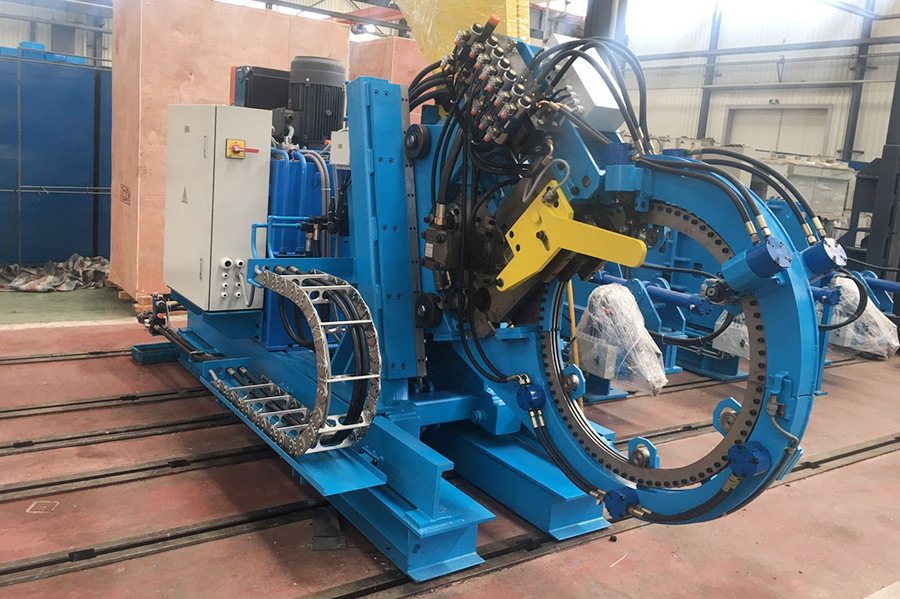
The shearing and butt welding machine is a single-blade hydraulic shear, with each pair of scissors usable on four sides. A trolley-type scrap bin is used to receive the sheared head and tail ends. The inlet and outlet pressure plates use hydraulic clamping to clamp the tail and head, and can move in and out separately to adjust the welding gap to achieve optimal requirements. The welding torch is fixed on a base driven by a DC motor, moves at a set speed, and performs welding on the weld seam. The welding is performed by a CO2 gas shielded welding machine with automatic/manual welding operation. The guide rollers use a combination of manual adjustment and hydraulic drive, allowing for quick opening and centering, and have a function to adjust for lateral misalignment of the weld seam.
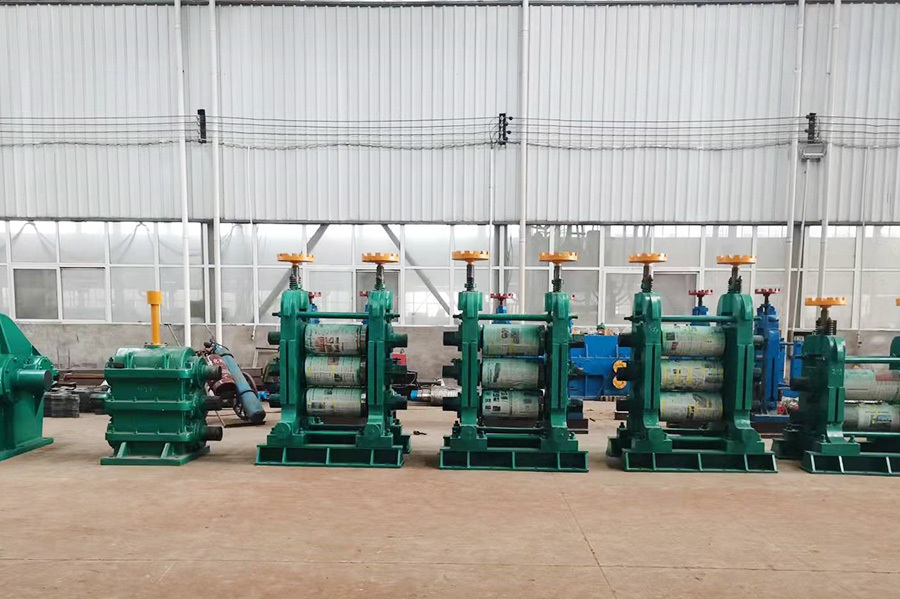
The steel strip after shearing and butt welding is fed to the steel strip combination feeding rollers (for the flanges) and the outlet feeding roller device (for the web) via the inlet feeding roller device. The speed of the inlet and outlet feeding rollers is adjusted by a hanging tension control device. At the same time, after passing through the torsion frame and a long S-shaped bend, the web plate enters the steel strip combination feeding roller device together with the upper and lower flanges. The top flange is rotated to form a straight line with the cut, and the edges of the top and bottom flange plates and three-phase clamping roller flange plates are smoothed by the edge adjustment device.
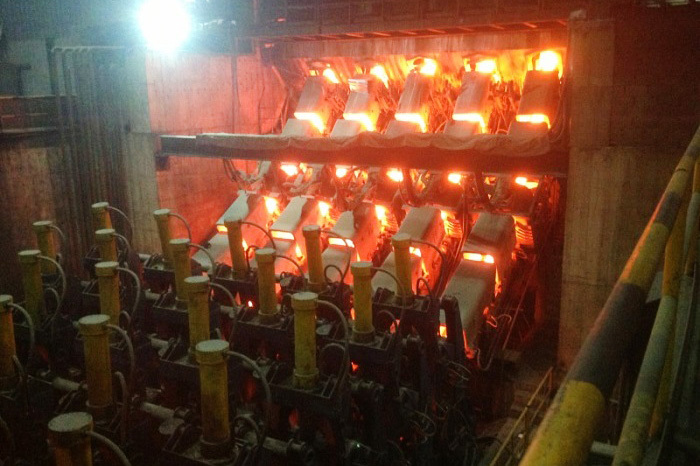
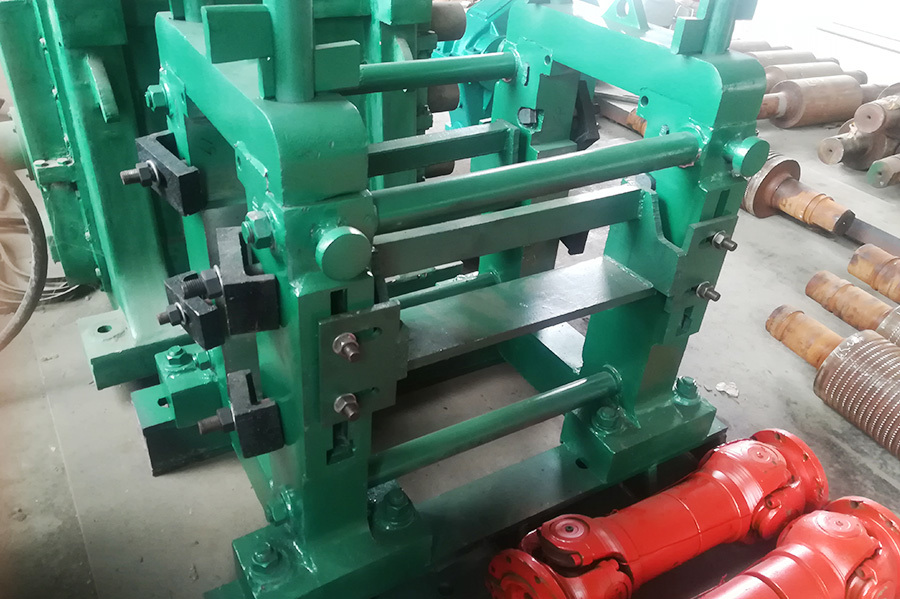
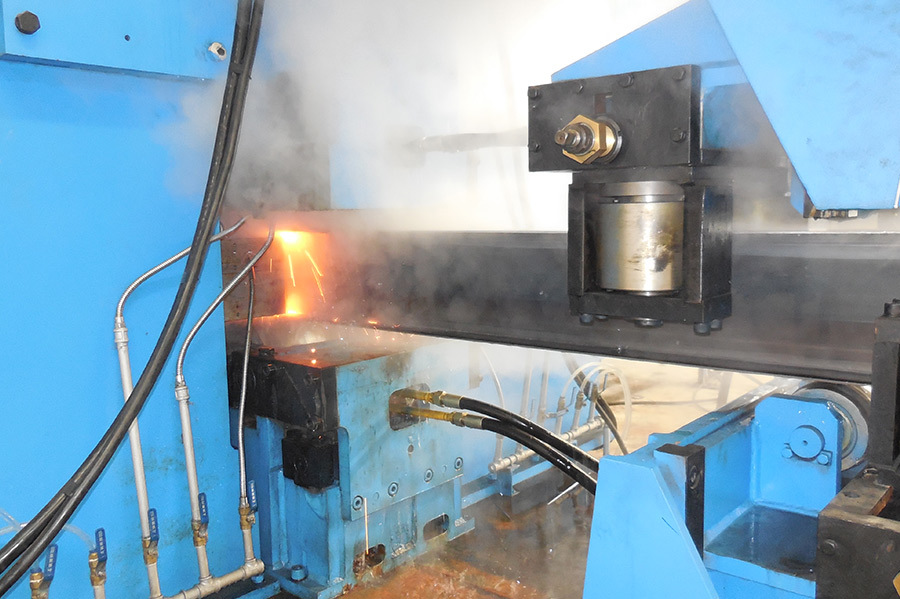
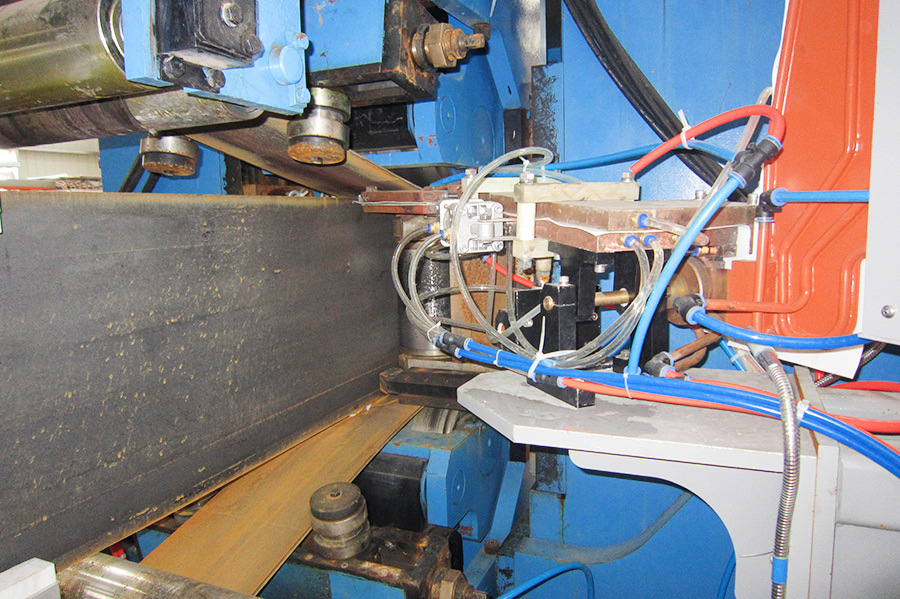
Three sets of steel strips are fed into the welding device. After the web plate is thickened, it enters the welding area with the flange plates. At the welding point, two extrusion rollers provide appropriate extrusion pressure. Welding is carried out under the voltage and current that meet the optimal welding requirements.
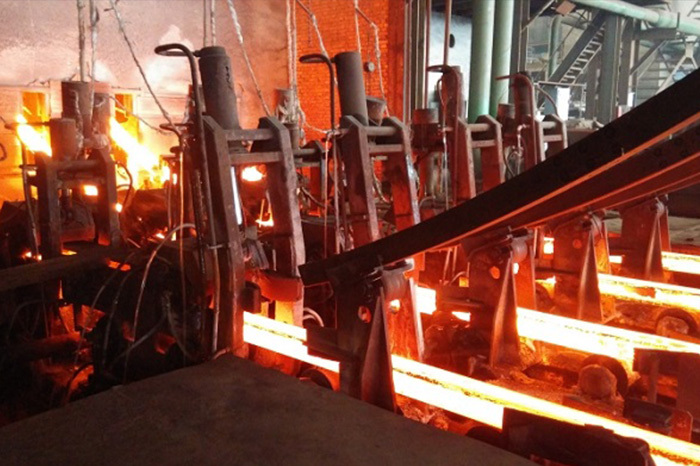
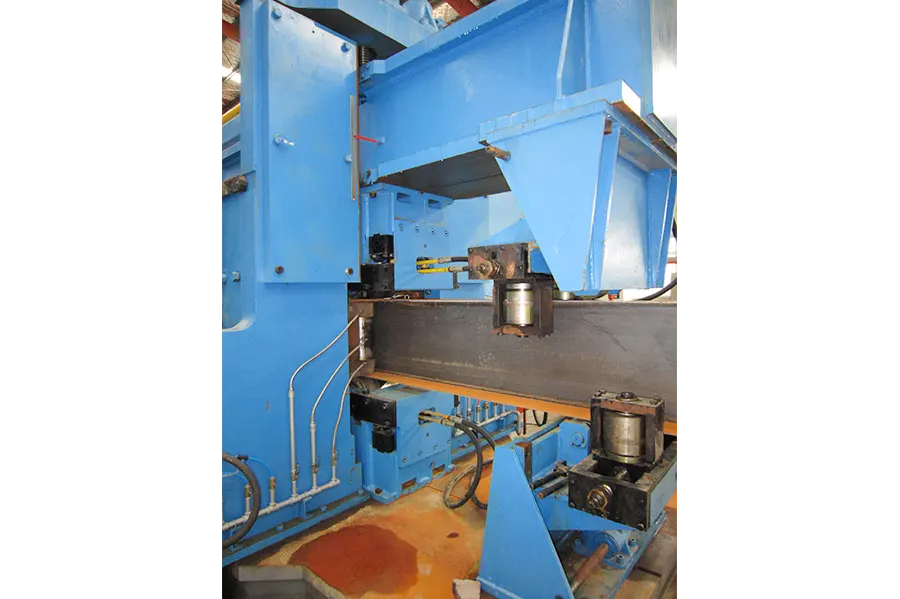
Two solid-state high-frequency contact welding machines weld the three strips together. The welded H-beam is pulled out by three pulling frames and sent to the cooling area. The flange plates are straightened by the flange straightening frame.
The H-beam flying saw cuts the steel beam into the required fixed length, and the cut steel beam is transported to the material platform.
Production Range
Typical Specifications mm×mm
Flange Width mm
Flange Thickness mm
Height mm
Web Thickness mm
Continuous Production Speed (Large Coil Raw Material) m/min
150×100
100
4.5
150
3.2
30
200×100
100
4.5
200
3.2
30
250×100
100
6.0
250
4.5
30
300×150
150
8.0
300
6.0
30
350×150
150
9.0
350
6.5
27
400×150
150
10.0
400
8.0
20
450×175
175
12.0
450
9.0
15
500×200
200
10.0
500
8.0
20
500×250
250
12.0
500
9.0
17
500×300
300
12.0
500
9.0
17
600×400
400
14.0
600
12.0
12
700×400
400
15.0
700
13.0
10
High-frequency welded H-beam production line - medium-sized
Still deciding? If you are interested, you need to take a sample first, Contact us!
Product Category
Tags
Metallurgical heavy machinery and equipment
Get a Quote
* Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication open. We will contact you as soon as possible.
Related Products
24-hour mobile phone:
Service Hotline
Service Email
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.